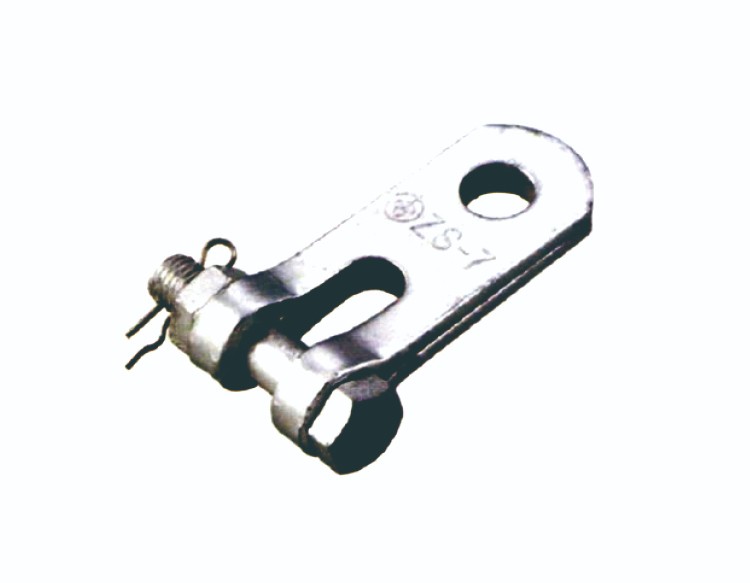
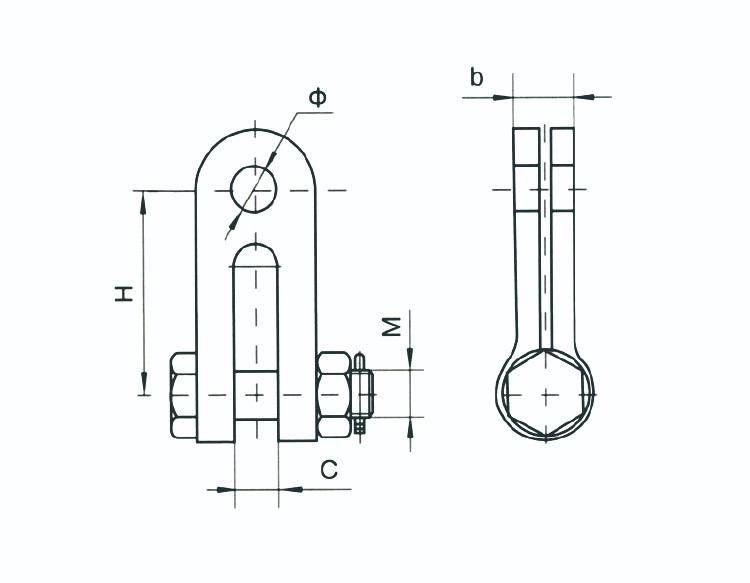
| Catalog No. | Dimensions(mm) | Failure Load(KN) | Weight(KG) | ||||||
| C | b | M | Φ | H | |||||
| ZS-7 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 80 | 70 | 0.6 | ||
| ZS-10 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 20 | 80 | 100 | 0.9 | ||
| ZS-12 | 22 | 22 | 22 | 24 | 80 | 120 | 1 | ||
| ZS-16 | 26 | 24 | 24 | 26 | 90 | 160 | 1.9 | ||
| ZS-25 | 33 | 30 | 30 | 33 | 120 | 250 | 4.33 | ||
| ZS-0780 | 18 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 80 | 70 | 0.6 | ||
| ZS-1080 | 20 | 18 | 18 | 20 | 80 | 100 | 0.9 | ||
1.Applications:
1)Linkage Systems: Clevises connect rods, levers, or other components, transmitting force or movement within machines.
2)Control Systems: Used in aircraft or industrial machinery for adjustable connections, enabling precise control over critical components.
3)Tie Rod Assemblies: Provide secure and adjustable connections between tie rods and other components, managing tension or compression forces.
4)Automotive Applications: Used in brake systems, suspension components, and more.
2.Types of Clevis Fasteners:
1)Shackles: The classic U-shaped clevis with a tang and clevis pin.
2)Brackets: Rectangular-shaped clevis with holes for bolts or screws.
3)Clevis Hangers: Used for hanging applications.
4)Clevis Rod Ends: Commonly found in mechanical linkages.