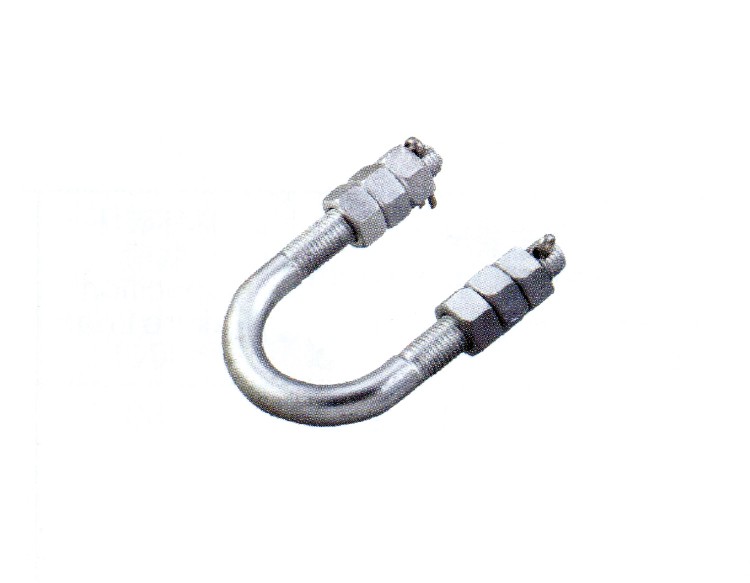
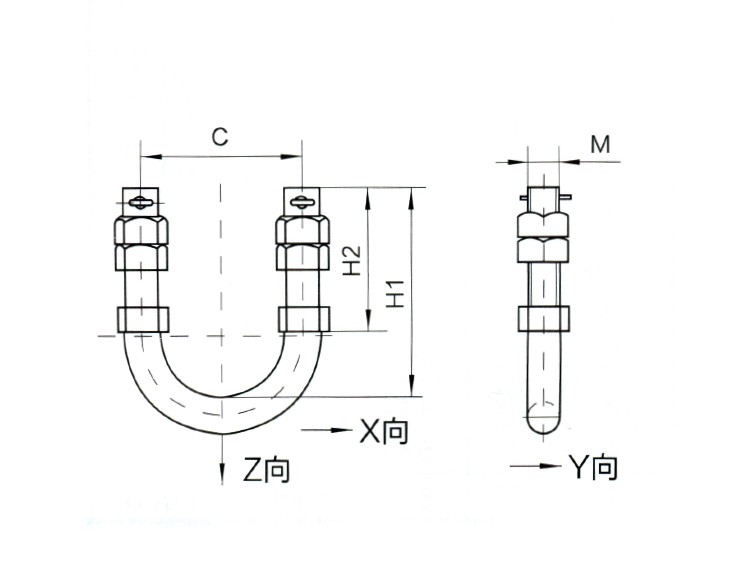
| Catalog No. | Dimensions(mm) | Failure Load(KN) | Weight(KG) | |||||||||
| C | M | H1 | H2 | X向 | Y向 | Z向 | ||||||
| U-1880 | 80 | 18 | 110 | 75 | 18 | 3.5 | 35 | 0.83 | ||||
| U-2080 | 80 | 20 | 120 | 80 | 24 | 4.9 | 47 | 1.08 | ||||
| U-2280 | 80 | 22 | 130 | 90 | 28 | 6.5 | 57 | 1.3 | ||||
1.Function and Applications:
1)U-bolts primarily serve as Rest+Guide+Hold down support for piping systems.
2)They can also be adapted to work as line stops with minor installation adjustments.
3)Common uses of U-bolts in piping solutions include:
(1)Providing lateral restraints to pipes.
(2)Supporting bare pipes smaller than 8 inches in diameter.
(3)Suppressing line vibrations by adding rigidity to the system.
(4)Supporting vertical elevated pipe runs.
(5)Preventing pipe movement and breakage during transportation.
2.Materials:
1)U-bolts can be manufactured from various strong and durable materials.
2)Widely used materials in the piping industry include:
(1)Plain Carbon Steel
(2)Stainless Steel
(3)Protective coatings (such as zinc plating, hot-dip galvanization, thermoplastic coating, and fluoropolymer coating) are added to prevent corrosion.
3.Types of U-Bolts:
1)Non-gripped U-bolt (U-bolt as Guide):
(1)Common and simple installation for pipe guiding.
(2)Does not restrict axial movement.
(3)Nuts are placed on the top and bottom of the support beam, leaving a gap between the pipe and the U-bolt surface.
2)Gripped U-bolt (U-bolt as Anchor):
(1)Functions as an anchor to stop pipe movement at the support location.
(2)Installed without space between the pipe and U-bolt.
(3)Both bolts are placed at the bottom of the secondary support structure and tightened against the pipe.